Monitoring, Debugging, and Performance Analysis for Pthreads
Monitoring and Debugging Pthreads
- Debuggers vary in their ability to handle Pthreads. The TotalView debugger is LC’s recommended debugger for parallel programs. It is well suited for both monitoring and debugging threaded programs.
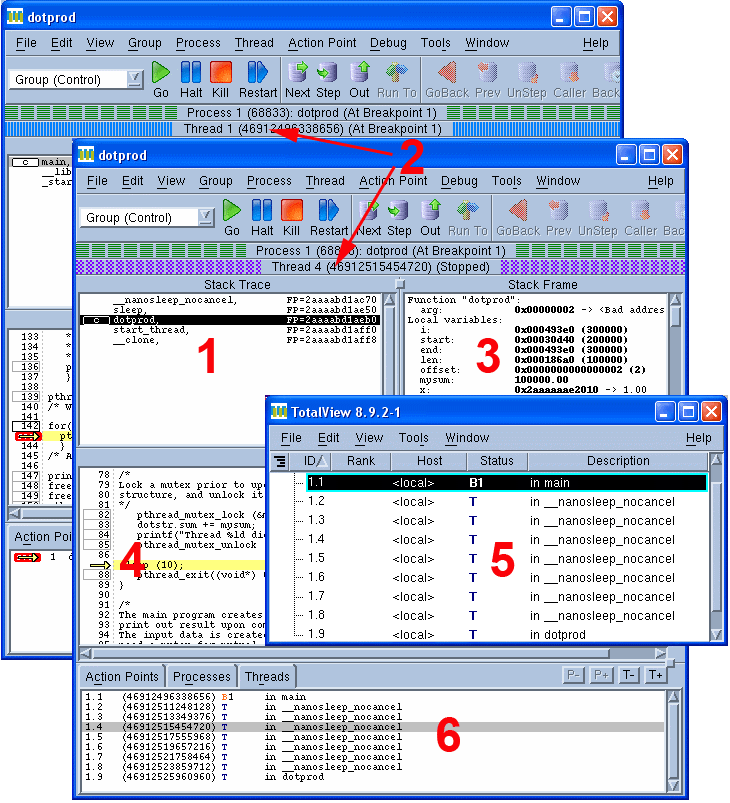
- An example screenshot from a TotalView session using a threaded code is shown below.
- Stack Trace Pane: Displays the call stack of routines that the selected thread is executing.
- Status Bars: Show status information for the selected thread and its associated process.
- Stack Frame Pane: Shows a selected thread’s stack variables, registers, etc.
- Source Pane: Shows the source code for the selected thread.
- Root Window showing all threads
- Threads Pane: Shows threads associated with the selected process
- See the TotalView Debugger tutorial for details.
- The Linux ps command provides several flags for viewing thread information. Some examples are shown below. See the man page for details.
% ps -Lf
UID PID PPID LWP C NLWP STIME TTY TIME CMD
blaise 22529 28240 22529 0 5 11:31 pts/53 00:00:00 a.out
blaise 22529 28240 22530 99 5 11:31 pts/53 00:01:24 a.out
blaise 22529 28240 22531 99 5 11:31 pts/53 00:01:24 a.out
blaise 22529 28240 22532 99 5 11:31 pts/53 00:01:24 a.out
blaise 22529 28240 22533 99 5 11:31 pts/53 00:01:24 a.out
% ps -T
PID SPID TTY TIME CMD
22529 22529 pts/53 00:00:00 a.out
22529 22530 pts/53 00:01:49 a.out
22529 22531 pts/53 00:01:49 a.out
22529 22532 pts/53 00:01:49 a.out
22529 22533 pts/53 00:01:49 a.out
% ps -Lm
PID LWP TTY TIME CMD
22529 - pts/53 00:18:56 a.out
- 22529 - 00:00:00 -
- 22530 - 00:04:44 -
- 22531 - 00:04:44 -
- 22532 - 00:04:44 -
- 22533 - 00:04:44 -
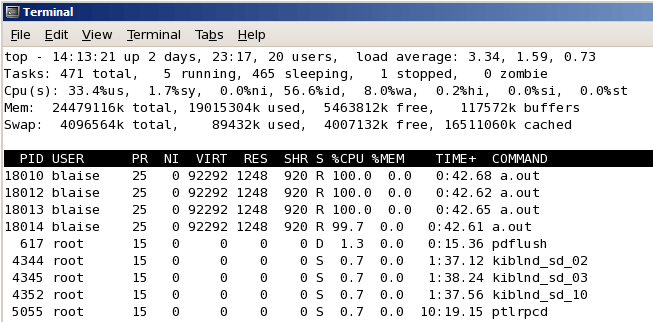
LC’s Linux clusters also provide the top command to monitor processes on a node. If used with the -H flag, the threads contained within a process will be visible. An example of the top -H command is shown below. The parent process is PID 18010 which spawned three threads, shown as PIDs 18012, 18013 and 18014.
Performance Analysis Tools:
- There are a variety of performance analysis tools that can be used with threaded programs. Searching the web will turn up a wealth of information.
- At LC, the list of supported computing tools can be found at: https://hpc.llnl.gov/software.
- These tools vary significantly in their complexity, functionality and learning curve. Covering them in detail is beyond the scope of this tutorial.
- Some tools worth investigating, specifically for threaded codes, include:
- Open|SpeedShop
- TAU
- HPCToolkit
- PAPI
- Intel VTune Amplifier
- ThreadSpotter
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory
|
7000 East Avenue • Livermore, CA 94550 | LLNL-WEB-458451
Operated by the Lawrence Livermore National Security, LLC for the
Department of Energy's National Nuclear Security Administration
Learn about the Department of Energy's Vulnerability Disclosure Program